According to reports from the aviation industry, India’s civil aviation sector has experienced remarkable growth over the past three years, making it one of the fastest-growing industries in the country. India has now become the third-largest domestic aviation market in the world and is projected to surpass the UK to become the third-largest air passenger market globally by 2024.
The air transport sector plays a crucial role in India’s economy, necessitating substantial efforts to develop the necessary infrastructure for continued growth. With its roots dating back to the 1930s, Indian aviation’s history is intertwined with Air India and state control. Here’s how India became the aviation hub it is today.
A Brief History of Civil Aviation in India
- Early Beginnings: February 18, 1911

The first civil aviation flight in India was a brief 15-minute demonstration from the United Provinces Industrial and Agricultural Exhibition in Allahabad to Naini, covering about 9.7 to 10 kilometres.
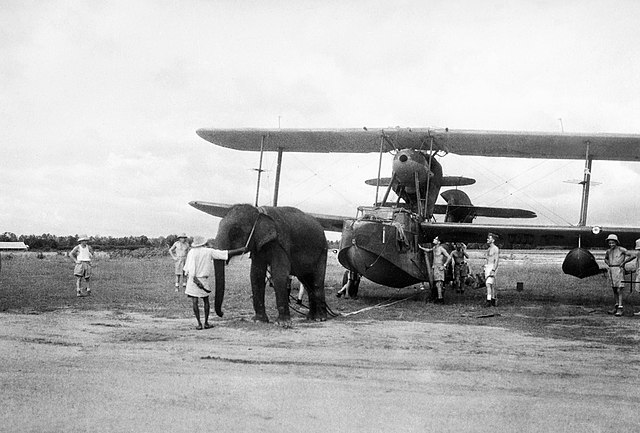
2. The Humber Aircraft
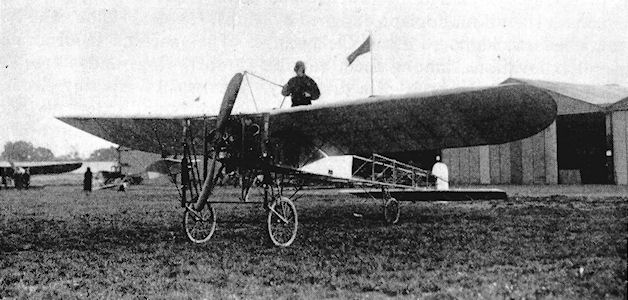
The Humber aircraft, used for carrying mail, had a wooden frame and was powered by a 50-horsepower engine. It transported 6,500 pieces of mail to Allahabad’s post office in around 13 to 15 minutes.
3. Henri Pequet’s Historic Flight
French pilot Henri Pequet flew the Humber aircraft, marking a significant milestone in Indian aviation in 1911.
4. J.R.D. Tata: The Father of Indian Civil Aviation

J.R.D. Tata, who opened a flying club in Bombay at the age of 24, became the first Indian with a flying license. He piloted the first flight in Indian aviation history and founded Tata Air Services, India’s first airline.
5. Tata Air Services: India’s First Airline
In 1932, Tata Air Services commenced operations, with its inaugural flight from Karachi to Mumbai on October 15, 1932. During World War II, Tata Airways played a crucial role in transporting troops and supplies for the British.
6. Transformation to Air India

In 1947, post-independence, Tata Airlines was renamed Air India, with Tata and the government holding a 49% stake.
Major Milestones in Indian Aviation
8. Boom in the Aviation Sector
By 1994, the deregulation of airline formation laws led to the emergence of private airlines like Jet Airways and ModiLuft, while Air India and Indian Airlines continued as government-run airlines.
9. Juhu Aerodrome: India’s First Airport

J.R.D. Tata’s airmail service from Karachi to Bombay landed at Juhu Aerodrome, marking the start of airline operations in India. Although initially promising, Juhu could not become a key airport due to critical flaws.
9. Cochin International Airport
The first international airport in India developed under the Public-Private Partnership model was Cochin International Airport in Kerala.
10. Indira Gandhi International Airport
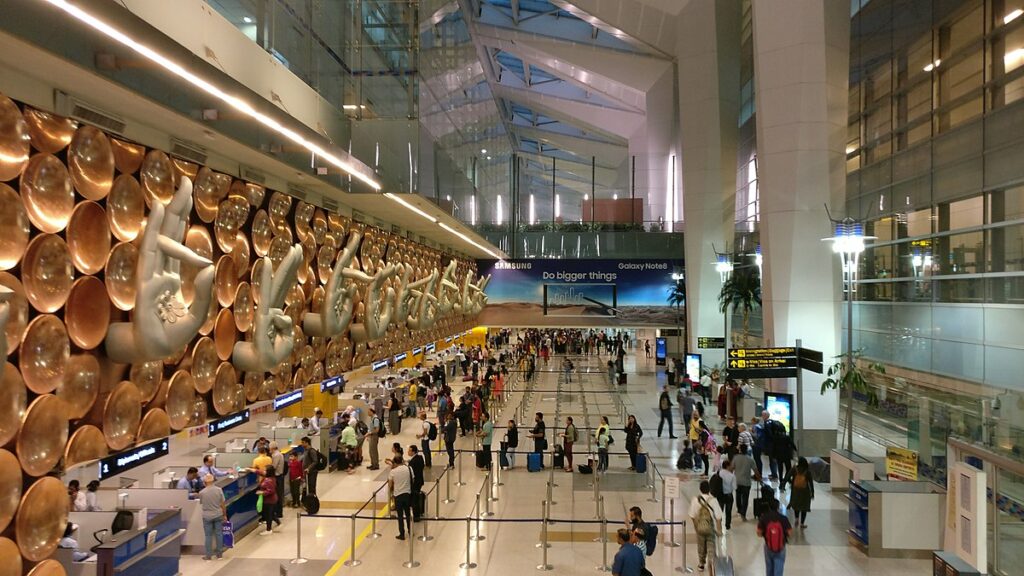

Declared the best airport by the Airports Council International’s Airport Service Quality Awards in the 25-40 million passengers category.
11. Kushok Bakula Rimpochee Airport
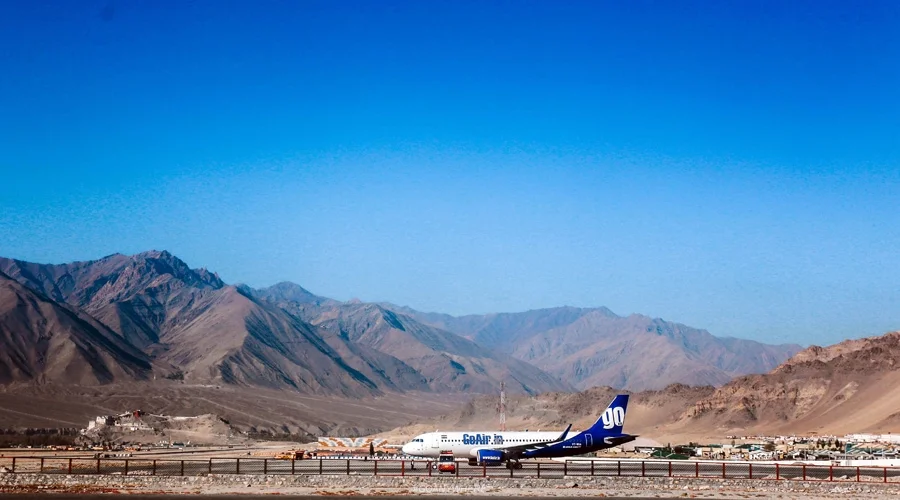

Located in Leh, this airport is one of the highest in the world, situated over 10,000 feet above sea level.
12. Trichy Airport: The Smallest Airport

Trichy Airport in Tamil Nadu is the smallest airport in India, with the shortest runway length.
13. Uttar Pradesh: The State with the Most Airports
Uttar Pradesh is set to have five international airports, the highest in the country, including the upcoming Jewar International Airport.
Current State of Indian Aviation
14. Airports in India
The Airports Authority of India (AAI) manages 137 airports, including 103 domestic, 34 international, and 10 customs airports.
15. Best Airports in 2024

Delhi’s Indira Gandhi International Airport and Bengaluru’s Kempegowda International Airport jointly won the best airport in India tag in 2024.
16. International Civil Aviation Day
Celebrated on December 7, this day aims to raise awareness about the importance of aviation in international air travel and economic development.
17. The 5/20 Rule

Indian airlines must have five years of domestic flying experience and at least 20 aircraft in their fleet to operate international flights.
18. Aircraft Hijackings
India has experienced three major aircraft hijackings: the 1971 Indian Airlines hijacking, Indian Airlines Flight 427 in 1993, and Indian Airlines Flight 814 in 1999.
19. India’s journey in civil aviation has been remarkable, evolving from a modest beginning to becoming a significant player on the global stage.
This article provides a comprehensive look into the rich history and rapid growth of civil aviation in India.